משתמש:Cohenjo
 |
דף זה אינו ערך אנציקלופדי
| |
| דף זה אינו ערך אנציקלופדי | |
{{[[תבנית:{{{1}}}|{{{1}}}]]}}
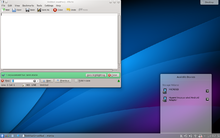

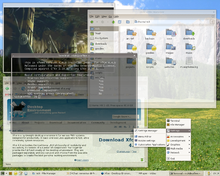
מנהל החלונות X הוא פרוטוקול תצוגה. הפרוטוקול מספק סט של כלים ליצירת ממשק משתמש גרפי (GUI) לרוב מערכות מבוססות UNIX והוסב למערכות הפעלה נוספות.
X מספק את התשתית הבסיסית לבניה של סביבות גרפיות: ציור והזזת חלונות, ממשק עם מקלדת ו/או עכבר וכו'.ככזה הוא אינו כופה את עיצוב הממשק ומאפשר לתוכניות לקבוע את העיצוב בעצמן, עקב כך ניתן לראות סביבות עבודה מבוססות X אשר שונות מאוד במראה ובעיצובן. X אינו חלק אינטגרלי ממערכת ההפעלה, הוא מגיע כשכבה נוספת מעל גרעין מערכת ההפעלה.
בניגוד לפרוטוקולי תצוגה קודמים, X תוכנן לעבוד על גבי רשתות תקשורת ולא למכשיר תצוגה. X מאפשר לאפליקציה לרוץ במכונה אחרת מאשר זו אשר בא מופיע הממשק למשתמש.
X נוצר ל MIT בשנת 1984. הגרסא הנוכחית, X11, הופיעה בספטמבר 1987. קרן X.org מובילה את פרויקט X, עם המימוש הנוכחי, X.org Server, זמין כתוכנה חופשית תחת רשיון MIT ורשיונות חופשיים דומים.
תכנון
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]X מבוסס מודל client-server: שרת X אשר מתקשר עם תוכנות לקוח שונות. השרת מקבל בקשות לפלט גרפי (חלונות) ושולח קלט אשר התקבל מהמשתמש (מהמקלדת, עכבר או אמצעי קלט אחר).
The server may function as:
- an application displaying to a window of another display system
- a system program controlling the video output of a PC
- a dedicated piece of hardware.
המינוח של client-server - כאשר המסוף של המשתמש הוא ה"שרת", והאפליקציה היא ה"לקוח" - נוטה לבלבל משתמשי X חדשים, שכן המונחים נראים הפוכים. אך המינוח נובע מנקודת המבט של X ולא של משתמש הקצה או החומרה: X משמש כשרת אשר לקוחות (אפליקציות) פונות אליו.
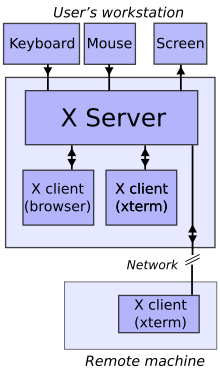
פרוטוקול התקשורת בין השרת והלקוח פועל בשקיפות מעל הרשת: הן הלקוח והן השרת יכולים לרוץ על אותה מכונה או מכונות נפרדות, ייתכן אף על ארכיטקטורות שונות ו/או מערכות הפעלה שונות, ללא כל שינוי. השרת והלקוח אף יכולים לתקשר בצורה מאובטחת על גבי האינטרנט על ידי Tunneling על גבי חיבור רשת מוצפן.
An X client itself may contain an X server having display of multiple clients. This is known as "X nesting". Open-source clients such as Xnest and Xephyr support such X nesting.
בכדי להציג תוכנה מרוחקת על שרת מקומי, המשתמש בדר"כ יפתח מסוף וtelnet או ssh לאפליקציה המרוחקת ויבקש שרותי תצוגה/קלט מקומיים (e.g. export DISPLAY=[user's machine]:0 on a remote machine running bash) האפליקציה אז מתחברת לשרת המקומי, המספק שרותי תצוגה וקלט למשתמש. אלטרנטיבה לזה היא הרצת תוכנת עזר אשר מתחברת למכונה המרוחקת ומפעילה את האפליקציה שם.
דוגמאות לתוכנות מרוחקות כוללות:
- ניהול מכונה מרחוק בסביבה גרפית
- הרצת סימולציה כבדת משאבים על שרת UNIX מרוחק והצגת הנתונים על מחשב Windows מקומי
עקרונות
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]בשנת 1984, בוב שיפלר Bob Scheifler וג'ים גטיס Jim Gettys ניסחו את העקרונות המנחים של X:
- לא להוסיף פונקציונאליות חדשה אלא אם המממש לא יכול להשלים אפליקציה אמיתית בלעדיה
- חשוב לקבוע מה מערכת היא לא כמו מה היא כן. אין צורך לענות על כל צרכי האנושות אלא לעצב את המערכת כך שכל צורך נוסף ניתן לתמוך קדימה
- הדבר היחיד שגרוע מהכללות מדוגמא אחת הוא הכללות ללא דוגמאות כלל
- אם בעיה אינה מובנת לחלוטין עדיף לא לספק לה פתרון
- אם ניתן להשיג 90% מהתוצאה הרצוייה ב10% של עבודה, תשתמש בפתרון הפשוט יותר (ראה גם גרוע זה טוב יותר)
- בודד סיבוכיות כמה שיותר
- ספק מנגמון ולא מדיניות. בפרט, מדיניות ממשק המשתמש הוא אחריות הקליינט
העיקרון הראשון שונה בעת העיצוב של X11 ל: "לא להוסיף פונקציונאליות חדשה אלא אם ידוע כי אפליקציה אמיתית תצטרך אותה."
X בגדול שמרה על עקרונותיה. המימוש מפותח בראיה להרחבות ושיפורים תוך תאימות מרבית לפרוטוקול המקורי מ 1987.
ממשק משתמש
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]X בכוונה אינו מגדיר את ממשק המשתמש, כגון כפתורים, תפריטים וכו'. במקום זה, תוכנות משתמש כגון מנהלי חלונות וסביבות עבודה או GUI של אפליקציות מגדירות את כל הפרטים הללו. כיוון שכך לא ניתן להצביע על תוכנת X "טיפוסית", שכן ברוב התקופות היו מספר ממשקים פופולריים בקרב משתמשים.
מנהל חלונות שולט במיקום ובמראה של חלונות האפליקציה.
A window manager controls the placement and appearance of application windows. This may have an interface akin to that of Microsoft Windows or of the Macintosh (examples include Metacity in GNOME, KWin in KDE or Xfwm in Xfce) or have radically different controls (such as a tiling window manager). The window manager may be bare-bones (e.g. twm, the basic window manager supplied with X, or evilwm, an extremely light window manager) or offer functionality verging on that of a full desktop environment (e.g. Enlightenment).
משתמשים רבים משתשים בX עם סביבת שולחן עבודה מלאה, אשר מכיל מנהל חלונות, אפליקציות שונות וממשק מוגדר. GNOME, KDE וXfce הם בין שולחנות העבודה הפופולריים יותר. הסביבת סטנדרט של UNIX (Unix standard ) היא CDE (Common Desktop Environment)
The freedesktop.org initiative addresses interoperability between desktops and the components needed for a competitive X desktop.
כיוון ש X אחראי לאינטראקציה של המקלדת והעכבר כל שולחן העבודה הגקפי, מספר קיצורי מקשים keyboard shortcut נקשרו עם X. Control-Alt-Backspace בדרך כלל מפסיק את פעולת מושב הX (session, בעוד ש Control-Alt בשילוב עם מקש פונק' function key מחליף למסוף וירטואלי virtual console מתאים. יש לציין, כי אלו פרטים אלו הושארו למימוש הפרטני של שרת ה X והם בשום אופן לא אוניברסלים; למשל, מימושי X לWindows ולMacintosh בדר"כ לא מספקים קיצורים אלו.
Implementations
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]The X.Org reference implementation serves as the canonical implementation of X. Due to the liberal licensing, a number of variations, both free and proprietary, have appeared. Commercial UNIX vendors have tended to take the reference implementation and adapt it for their hardware, usually customising it heavily and adding proprietary extensions. תבנית:Wrapper left | |- |}
Up to 2004, XFree86 provided the most common X variant on free Unix-like systems. XFree86 started as a port of X for 386-compatible PCs and, by the end of the 1990s, had become the greatest source of technical innovation in X and the de facto standard of X development.[1] Since 2004, however, the X.Org reference implementation, a fork of XFree86, has become predominant.
While computer aficionados most often associate X with Unix, X servers also exist natively within other graphical environments. Hewlett-Packard's OpenVMS operating system includes a version of X with CDE, known as DECwindows, as its standard desktop environment. Apple's Mac OS X v10.3 (Panther) and up includes X11.app, based on XFree86 4.3 and X11R6.6, with better Mac OS X integration. Third-party servers under Mac OS 7, 8 and 9 included MacX.
Microsoft Windows does not come with support for X, but many third-party implementations exist, both free software such as Cygwin/X, Xming, WeirdMind and WeirdX; and proprietary products such as MKS X/Server, Reflection X, Xmanager, X-Deep/32, WiredX, Exceed and X-Win32. They normally serve to control remote X clients.
When another windowing system (such as those of Microsoft Windows or Mac OS) hosts X, the X system generally runs "rootless", meaning the host windowing environment looks after the root window (the background and associated menus) and manages the geometry of the hosted X windows — although some servers (Xmanager, and Exceed, for example) can also create the root window for the remote clients to display to as a separate window in the host system.
מסופי X
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]
מסוף X הוא "לקוח רזה" thin client אשר רץ כשרת X. ארכיטקטורה זו נהייתה נפוצה לבניית פארק מסופים המאפשר למשתמשים רבים לגשת בו זמנית לאותו שרת מרכזי. שימוש זה עומד בקו עם המטרה המקורית של הפרויקט של MIT.
מסופי X סורקים את הרשת (המקומית broadcast domain ) ע"י שימוש ב X Display Manager Control Protocol ליצירת רשימה של מארחים (שרתים) אשר ניתן להריץ מהן לקוחות. על המארח להריץ מנהל תצוגה X display manager.
מסופי X יעודיים (מבוססי חומרה) נהיו פחות נפוצים; מחשבים אישיים או לקוחות דקים מודרניים עם שרת X, מאפשרים בדר"כ את אותה הפונקציונאליות במחיר נמוך יותר.
Limitations and criticisms of X
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]The UNIX-HATERS Handbook (1994) devoted an entire chapter[2], to the problems of X. Why X Is Not Our Ideal Window System (1990) by Gajewska, Manasse and McCormack detailed problems in the protocol with recommendations for improvement.
User interface features
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]X deliberately contains no specification as to user interface or most inter-application communication. This has resulted in several vastly different interfaces, and in applications that have not always worked well together. The ICCCM, a specification for client interoperability, has a reputation as difficult to implement correctly. Further standards efforts such as Motif and CDE did not remedy matters. This has frustrated users and programmers for a long time.[3] Graphics programmers now generally address consistency of application look and feel and communication by coding to a specific desktop environment or to a specific widget toolkit, which also avoids having to deal directly with the ICCCM.
The X protocol provides no facilities for handling audio, leaving it to the operating system or audio systems like OSS or ALSA to provide support for audio hardware and sound playback. Most programmers simply use local, OS-specific sound APIs. The first generation of client-server sound systems included rplay and Network Audio System. More recent efforts have produced EsounD (GNOME), aRts (KDE), and PulseAudio to name a few. In 2001, the X.org foundation announced the development of the Media Application Server (MAS) to remedy this problem. However, none of these are generally used as a solution to the problem.
Network
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]
An X client cannot generally be detached from one server and reattached to another, as with Virtual Network Computing (VNC), though certain specific applications and toolkits are able to provide this facility.[4] Workarounds (VNC :0 viewers) also exist to make the current X-server screen available via VNC.
Network traffic between an X server and remote X clients is not encrypted by default. An attacker with a packet sniffer can intercept it, making it possible to view anything displayed to or sent from the user's screen. The most common way to encrypt X traffic is to tunnel it over SSH.
Client-server separation
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]X's design requires the clients and server to operate separately, and device independence and the separation of client and server incur overhead compared to an operating system where the graphics are integrated into the OS, such as early versions of Microsoft Windows or Mac OS. X advocates recommended 4 to 8 MB of RAM for reasonable performance; until the mid-1990s, this seemed bloated compared to Windows or Mac OS.
Current versions of Windows and Mac OS X Quartz have internal subsystem separation similar to the client/server divide in X and comparable performance and higher resource usage to X with KDE or GNOMEתבנית:Fact. Most of the overhead comes from network round-trip delay time between client and server (latency rather than from the protocol itself): the best solutions to performance issues involve paying attention to application design.[5] A common misconception is that X's network features result in excessive complexity if only used locally, and that X's network capabilities cause an undesirable performance hit; modern X implementations use local sockets and shared memory, requiring very little overhead.
מתחרים לX
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]לצורכי גרפיקה, כמעט כל המערכות דמויות UNIX משתמשות ב X. אף על פי כן, נכתבו אלטרנטיבות לX. אלטרנטיבות היסטוריות כוללות את NeWS של חברת Sun, אשר נחלה כשלון בשוק וכן Quartz של מ"ה Mac OS X של חברת Apple.
מייק פקוט (Mike Paquette), אחד מהכותבים של Quartz, הסביר מדוע אפל לא עברה מPostScript לX, אלא במקום החליטה לפתח מנהל חלומות עצמאי באומרו כי לאחר שאפל הייתה מוסיפה תמיכה לכל המאפיינים שהיא רצתה להוסיף לX11, לא נותר דמיון רב לX11 והוא לא היה תואם לשרתים אחרים בלוא וכי. [6]
נסיונות נוספים לטפל בביקורת על X ע"י החלפתו לגמרי כוללים את Berlin/Fresco ואת Y Window System. אך נסיונות אלו לא קיבלו תמיכה, ופרשנים רבים מטילים ספק בחיות של כל תחליף אשר לא שומר תאימות לאחור עם X.
Other competitors attempt to avoid the overhead of X by working directly with the hardware. Such projects include DirectFB and the very small FBUI. The Direct Rendering Infrastructure (DRI), which aims to provide a reliable kernel-level interface to the framebuffer, may make these efforts redundant. However, in Linux embedded systems requiring real-time capabilities (e.g. using RTAI), the use of hardware acceleration via DRI is discouraged; X may be unsuitable for such applications.
Other ways to achieve network transparency for graphical services include:
- the SVG Terminal, a protocol to update Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) content in a browser in near-real-time
- Virtual Network Computing (VNC), a very low-level system which sends compressed bitmaps across the network; the Unix implementation includes an X server
- Citrix Presentation Server, an X-like product for Microsoft Windows
- Tarantella, which provides a Java client for use in web browsers
- RAWT, IBM's Java-only Remote AWT, which implements a Java "server" and simple hooks for any remote Java client
היסטוריה
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]אבות קדמונים
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]מספר מערכות תצוגה מבוססות מפות סיבית (bitmaps) קדמו לX. מחברת Xerox הגיעו Alto בשנת 1973 ומערכת Star משנת 1981. מאפל הגיעו Lisa בשנת 83 וMacintosh בשנת 84. בעולם הUNIX היה את Andrew Project ואת Blit מאת רוב פיק (Rob Pike) בשנת 84'.
X קיבל את שמו כיורש של מערכת חלומות אשר נקראה W (האות X מופיעה לאחר W באלף-בית הלטיני). W רץ תחת מ"ה V operating system. מערכת W השתמשה בפרוטוקול רשת אשר תמך במסופים ובחלונות כאשר השרת שומר רשימות תצוגה.

מקור ופיתוח מוקדם
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]Origin and early development
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]The original idea of X emerged at MIT in 1984 as a collaboration between Jim Gettys (of Project Athena) and Bob Scheifler (of the MIT Laboratory for Computer Science). Scheifler needed a usable display environment for debugging the Argus system. Project Athena (a joint project between Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC), MIT and IBM to provide easy access to computing resources for all students) needed a platform-independent graphics system to link together its heterogeneous multiple-vendor systems; the window system then under development in Carnegie Mellon University's Andrew Project did not make licenses available, and no alternatives existed.
The project solved this by creating a protocol that could both run local applications and call on remote resources. In mid-1983 an initial port of W to Unix ran at one-fifth of its speed under V; in May 1984, Scheifler replaced the synchronous protocol of W with an asynchronous protocol and the display lists with immediate mode graphics to make X version 1. X became the first windowing system environment to offer true hardware-independence and vendor-independence.
Scheifler, Gettys and Ron Newman set to work and X progressed rapidly. They released Version 6 in January 1985. DEC, then preparing to release its first Ultrix workstation, judged X the only windowing system likely to become available in time. DEC engineers ported X6 to DEC's QVSS display on MicroVAX.
In the second quarter of 1985 X acquired color support to function in the DEC VAXstation-II/GPX, forming what became version 9. Although MIT had licensed X6 to some outside groups for a fee, it decided at this time to license X9 and future versions under what became known as the MIT License. X9 appeared in September 1985.
A group at Brown University ported version 9 to the IBM RT/PC, but problems with reading unaligned data on the RT forced an incompatible protocol change, leading to version 10 in late 1985. By 1986, outside organizations had started asking for X. The release of X10R2 took place in January 1986; that of X10R3 in February 1986. X10R3 became the first version to achieve wide deployment, with both DEC and Hewlett-Packard releasing products based on it. Other groups ported X10 to Apollo and to Sun workstations and even to the IBM PC/AT. Demonstrations of the first commercial application for X (a mechanical computer-aided engineering system from Cognition Inc. that ran on VAXes and displayed on PCs running an X server) took place at the Autofact trade show at that time. The last version of X10, X10R4, appeared in December 1986.
Attempts were made to enable X servers as real-time collaboration devices, much as Virtual Network Computing (VNC) would later allow a desktop to be shared. One such early effort was Philip J. Gust's SharedX tool.
Although X10 offered interesting and powerful functionality, it had become obvious that the X protocol could use a more hardware-neutral redesign before it became too widely deployed; but MIT alone would not have the resources available for such a complete redesign. As it happened, DEC's Western Software Laboratory found itself between projects. Smokey Wallace of DEC WSL and Jim Gettys proposed that DEC WSL build X11 and make it freely available under the same terms as X9 and X10. This process started in May 1986, with the protocol finalised in August. Alpha-testing of the software started in February 1987, beta-testing in May; the release of X11 finally occurred on September 15, 1987.
The X11 protocol design, led by Scheifler, got extensively discussed on open mailing lists on the nascent Internet that were bridged to USENET newsgroups. X therefore represents one of the first very large-scale free software projects.
The MIT X Consortium and the X Consortium, Inc.
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]In 1987, with the success of X11 becoming apparent, MIT wished to relinquish the stewardship of X, but at a June 1987 meeting with nine vendors, the vendors told MIT that they believed in the need for a neutral party to keep X from fragmenting in the marketplace. In January 1988, the MIT X Consortium formed as a non-profit vendor group, with Scheifler as director, to direct the future development of X in a neutral atmosphere inclusive of commercial and educational interests. Jim Fulton joined in January 1988 and Keith Packard in March 1988 as senior developers, with Jim focusing on Xlib, fonts, window managers, and utilities; and Keith re-implementing the server. Donna Converse and Chris D. Peterson joined later that year, focusing on toolkits and widget sets, working closely with Ralph Swick of MIT Project Athena. The MIT X Consortium produced several significant revisions to X11, the first (Release 2 - X11R2) in February 1988.
In 1993, the X Consortium, Inc. (a non-profit corporation) formed as the successor to the MIT X Consortium. It released X11R6 on May 16, 1994. In 1995 it took over stewardship of the Motif toolkit and of the Common Desktop Environment for Unix systems. The X Consortium dissolved at the end of 1996, producing a final revision, X11R6.3, and a legacy of increasing commercial influence in the development.[7][8]
The Open Group
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]In mid-1997 the X Consortium passed stewardship of X to The Open Group, a vendor group formed in early 1996 by the merger of the Open Software Foundation and X/Open.
The Open Group released X11R6.4 in early 1998. Controversially, X11R6.4 departed from the traditional liberal licensing terms, as the Open Group sought to assure funding for X's development.[9] The new terms would have prevented its adoption by many projects (such as XFree86) and even by some commercial vendors. After XFree86 seemed poised to fork, the Open Group relicensed X11R6.4 under the traditional license in September 1998.[10] The Open Group's last release came as X11R6.4 patch 3.
X.Org and XFree86
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]XFree86 originated in 1992 from the X386 server for IBM PC compatibles included with X11R5 in 1991, written by Thomas Roell and Mark W. Snitily and donated to the MIT X Consortium by Snitily Graphics Consulting Services (SGCS). XFree86 evolved over time from just one port of X to the leading and most popular implementation and the de facto steward of X's development.[11]
In May 1999, the Open Group formed X.Org. X.Org supervised the release of versions X11R6.5.1 onward. X development at this time had become moribund[12]; most technical innovation since the X Consortium had dissolved had taken place in the XFree86 project.[13] In 1999, the XFree86 team joined X.Org as an honorary (non-paying) member[14], encouraged by various hardware companies[15] interested in using XFree86 with Linux and in its status as the most popular version of X.
By 2003, while the popularity of Linux (and hence the installed base of X) surged, X.Org remained inactive[16], and active development took place largely within XFree86. However, considerable dissent developed within XFree86. The XFree86 project suffered from a perception of a far too cathedral-like development model; developers could not get CVS commit access[17][18] and vendors had to maintain extensive patch sets.[19] In March 2003 the XFree86 organization expelled Keith Packard, who had joined XFree86 after the end of the original MIT X Consortium, with considerable ill-feeling.[20][21][22]
X.Org and XFree86 began discussing a reorganisation suited to properly nurturing the development of X.[23][24][25] Jim Gettys had been pushing strongly for an open development model since at least 2000.[26] Gettys, Packard and several others began discussing in detail the requirements for the effective governance of X with open development.
Finally, in an echo of the X11R6.4 licensing dispute, XFree86 released version 4.4 in February 2004 under a more restricted license which many projects relying on X found unacceptable.[27] The added clause to the license was based upon the original BSD license's advertising clause, which was viewed by the Free Software Foundation and Debian as incompatible with the GNU General Public License.[28] Other groups saw further restrictions as being against the spirit of the original X (OpenBSD threatening a fork, for example). The license issue, combined with the difficulties in getting changes in, left many feeling the time was ripe for a fork.[29]
The X.Org Foundation
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]In early 2004 various people from X.Org and freedesktop.org formed the X.Org Foundation, and the Open Group gave it control of the x.org domain name. This marked a radical change in the governance of X. Whereas the stewards of X since 1988 (including the previous X.Org) had been vendor organizations, the Foundation was led by software developers and used community development based on the bazaar model, which relies on outside involvement. Membership was opened to individuals, with corporate membership being in the form of sponsorship. Several major corporations such as Hewlett-Packard and Sun Microsystems currently support the X.Org Foundation.
The Foundation takes an oversight role over X development: technical decisions are made on their merits by achieving rough consensus among community members. Technical decisions are not made by the board of directors; in this sense, it is strongly modelled on the technically non-interventionist GNOME Foundation. The Foundation does not employ any developers.
The Foundation released X11R6.7, the X.Org Server, in April 2004, based on XFree86 4.4RC2 with X11R6.6 changes merged. Gettys and Packard had taken the last version of XFree86 under the old license and, by making a point of an open development model and retaining GPL compatibility, brought many of the old XFree86 developers on board.[30]
X11R6.8 came out in September 2004. It added significant new features, including preliminary support for translucent windows and other sophisticated visual effects, screen magnifiers and thumbnailers, and facilities to integrate with 3D immersive display systems such as Sun's Project Looking Glass and the Croquet project. External applications called compositing window managers provide policy for the visual appearance.
On December 21, 2005[31] , X.Org released X11R6.9, the monolithic source tree for legacy users, and X11R7.0, the same source code separated into independent modules, each maintainable in separate projects.[32] The Foundation released X11R7.1 on May 22, 2006, about four months after 7.0, with considerable feature improvements.[33]
כיוונים עתידיים
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]עם קרן X.Org ו freedesktop.org, הקו הראשי של פיתוח X החל שוב להתפתח בקצב מהיר. המפתחים מתכוונים לשחרר גרסאות עתידיות כמוצר שמיש, ולא רק כבסיס ליצרנים לבנות מוצרים על בסיסו.
בכדי לאפשר צירופים רבים ככל האפשר של חומרה ומערכות הפעלה, X.Org מתכננים לגשת לחומרה רק דרך OpenGL ו Direct Rendering Infrastructure . ה DRI הופיע לראשונה ב XFree86 גרסא 4.0 והפך לסטנדרט החל מגרסא X11R6.7 והלאה. .[34] מערכות הפעלה רבות החלו להוסיף לגרעין מ"ה תמיכה במניפולציות חומרה. עבודה זו גדלה בהתמדה.
Nomenclature
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]People in the computer trade commonly shorten the phrase "X Window System" to "X11" or simply to "X". The term "X Windows" (in the manner of "Microsoft Windows") is not officially endorsed, though it has been in common use since early in the history of X and has been used deliberately for literary effect, for example in the UNIX-HATERS Handbook.[35]
====================================================================================================================================
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]היסטורית גרסאות
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]| גרסא | תאריך שחרור | שינויים מרכזיים |
|---|---|---|
| X1 | June 1984 | First use of the name "X"; fundamental changes distinguishing the product from W. |
| X6 | January 1985 | First version licensed to a handful of outside companies. |
| X9 | September 1985 | Color. First release under MIT License. |
| X10 | late 1985 | IBM RT/PC, AT (running DOS), and others |
| X10R2 | January 1986 | |
| X10R3 | February 1986 | First release outside MIT. uwm made standard window manager. |
| X10R4 | December 1986 | Last version of X10. |
| X11 | September 15, 1987 | First release of the current protocol. |
| X11R2 | February 1988 | First X Consortium release.[36] |
| X11R3 | October 25, 1988 | XDM |
| X11R4 | December 22, 1989 | XDMCP, twm brought in as standard window manager, application improvements, Shape extension, new fonts. |
| X11R5 | September 5, 1991 | PEX, Xcms (color management), font server, X386, X video extension |
| X11R6 | May 16, 1994 | ICCCM v2.0; Inter-Client Exchange; X Session Management; X Synchronization extension; X Image extension; XTEST extension; X Input; X Big Requests; XC-MISC; XFree86 changes. |
| X11R6.1 | March 14, 1996 | X Double Buffer extension; X keyboard extension; X Record extension. |
| X11R6.2 X11R6.3 (Broadway) |
December 23, 1996 | Web functionality, LBX. Last X Consortium release. X11R6.2 is the tag for a subset of X11R6.3 with the only new features over R6.1 being XPrint and the Xlib implementation of vertical writing and user-defined character support.[37] |
| X11R6.4 | March 31, 1998 | Xinerama.[38] |
| X11R6.5 | Internal X.org release; not made publicly available. | |
| X11R6.5.1 | August 20, 2000 | |
| X11R6.6 | April 4, 2001 | Bug fixes, XFree86 changes. |
| X11R6.7.0 | April 6, 2004 | First X.Org Foundation release, incorporating XFree86 4.4rc2. Full end-user distribution. Removal of XIE, PEX and libxml2.[39] |
| X11R6.8.0 | September 8, 2004 | Window translucency, XDamage, Distributed Multihead X, XFixes, Composite, XEvIE. |
| X11R6.8.1 | September 17, 2004 | Security fix in libxpm. |
| X11R6.8.2 | February 10, 2005 | Bug fixes, driver updates. |
| X11R6.9 X11R7.0 |
December 21, 2005 | EXA, major source code refactoring.[40] From the same source-code base, the modular autotooled version became 7.0 and the monolithic imake version was frozen at 6.9. |
| X11R7.1 | May 22, 2006 | EXA enhancements, KDrive integrated, AIGLX, OS and platform support enhancements.[41] |
| X11R7.2 | February 15, 2007 | Removal of LBX and the built-in keyboard driver, X-ACE, XCB, autoconfig improvements, cleanups.[42] |
| X11R7.3 | September 6, 2007 | Input hotplug, output hotplug (RandR 1.2), DTrace probes, PCI domain support.[43] |
גרסאה מוצעת
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]| גרסא | תאריך הוצאה | שינויים מרכזיים |
|---|---|---|
| X11R7.4 | Feb, 2008[44] | XGE, XACE, RandR 1.3 (GPU object), input transformation, pci-rework, XKB 2, _X_EXPORT, DRI memory manager, GLX 1.4, Glucose.[45] |
כותרת
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]הערות שוליים
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]- ^ Announcement: Modification to the base XFree86(TM) license. 02 Feb 2004
- ^ "The X-Windows Disaster"
- ^ Re: X is painful 15 Nov 1996
- ^ SNAP Computing and the X Window System 2005
- ^ An LBX Postmortem 2001-1-24
- ^ Why Apple didn't use X for the window system August 19, 2007
- ^ Financing Volunteer Free Software Projects 10 Jun 2005
- ^ Lessons Learned about Open Source 2000
- ^ X statement 02 Apr 1998
- ^ X11R6.4 Sample Implementation Changes and Concerns
- ^ Announcement: Modification to the base XFree86(TM) license. 02 Feb 2004
- ^ Q&A: The X Factor February 04, 2002
- ^ The Evolution of the X Server Architecture 1999
- ^ A Call For Open Governance Of X Development 23 Mar 2003
- ^ XFree86 joins X.Org as Honorary Member Dec 01, 1999
- ^ Another teleconference partial edited transcript 13 Apr 2003
- ^ Keith Packard issue 20 Mar 2003
- ^ Cygwin/XFree86 - No longer associated with XFree86.org 27 Oct 2003
- ^ On XFree86 development 9 Jan 2003
- ^ Invitation for public discussion about the future of X 20 Mar 2003
- ^ A Call For Open Governance Of X Development 21 Mar 2003
- ^ Notes from a teleconference held 2003-3-27 03 Apr 2003
- ^ A Call For Open Governance Of X Development 24 Mar 2003
- ^ A Call For Open Governance Of X Development 23 Mar 2003
- ^ Discussing issues 14 Apr 2003
- ^ Lessons Learned about Open Source 2000
- ^ XFree86 4.4: List of Rejecting Distributors Grows Feb 18, 2004
- ^ Appendix A: The Cautionary Tale of XFree86 June 5, 2002
- ^ X Marks the Spot: Looking back at X11 Developments of Past Year Feb 25, 2004
- ^ Appendix A: The Cautionary Tale of XFree86 June 5, 2002
- ^ X11R6.9 and X11R7.0 Officially Released December 21 2005
- ^ Modularization Proposal 2005-03-31
- ^ Proposed Changes for X11R7.1 2006-04-21
- ^ Getting X Off The Hardware July, 2004
- ^ X - a portable, network-transparent window system February 2005
- ^ The X Window System: History and Architecture 1 September 1999
- ^ XFree86 and X11R6.3 December 1999
- ^ The Open Group Announces Internet-Ready X Window System X11R6.4 March 31, 1998
- ^ X.Org Foundation releases X Window System X11R6.7 April 7, 2004
- ^ Changes Since R6.8 2005-10-21
- ^ Release Notes for X11R7.1 22 May 2006
- ^ The X.Org Foundation released 7.2.0 (aka X11R7.2) February 15th, 2007
- ^ X server version 1.4 release plans, accessed 2007-08-25
- ^ Debian X.org notes - X.org 7.4 plans - What we expect for Lenny (Brice Goglin, 11 September 2007)
- ^ XDS 2007 notes
לקריאה נוספת
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]- Hania Gajewska, Mark S. Manasse and Joel McCormack, Why X Is Not Our Ideal Window System (PDF), Software — Practice & Experience vol 20, issue S2 (October 1990)
- Linda Mui and Eric Pearce, X Window System Volume 8: X Window System Administrator's Guide for X11 Release 4 and Release 5, 3rd edition (O'Reilly and Associates, July 1993; softcover ISBN 0-937175-83-8)
- The X-Windows Disaster (UNIX-HATERS Handbook)
- Robert W. Scheifler and James Gettys: X Window System: Core and extension protocols: X version 11, releases 6 and 6.1, Digital Press 1996, ISBN 1-55558-148-X
- The Evolution of the X Server Architecture (Keith Packard, 1999)
- The means to an X for Linux: an interview with David Dawes from XFree86.org (Matthew Arnison, CAT TV, June 1999)
- Lessons Learned about Open Source (Jim Gettys, USENIX 2000 talk on the history of X)
- On the Thesis that X is Big/Bloated/Obsolete and Should Be Replaced (Christopher B. Browne)
- Open Source Desktop Technology Road Map (Jim Gettys, 09 December 2003)
- X Marks the Spot: Looking back at X11 Developments of Past Year (Oscar Boykin, OSNews, 25 February 2004)
- Getting X Off The Hardware (Keith Packard, July 2004 Ottawa Linux Symposium talk)
- Why Apple didn't use X for the window system (Mike Paquette, Apple Computer)
- The Cautionary Tale of XFree86 (from Make Your Open Source Software GPL-Compatible. Or Else. by David A. Wheeler, 16 February 2005)
- X Man Page (Retrieved on 2 February 2007)
- SNAP Computing and the X Window System (Jim Gettys, 2005)
ראו גם
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]- History of the graphical user interface
- X11 color names
- Xgl
- General Graphics Interface
- VirtualGL
- rio (program)
- List of Unix programs
- DESQview/X
- Cairo (graphics)
- Y Window System
- XFree86
קישורים חיצוניים
[עריכת קוד מקור | עריכה]- X.Org Foundation Official website
- The X Window System: A Brief Introduction
- Window managers for X
- The State of Linux Graphics (Jon Smirl, 30 August 2005)
- Writing a Graphics Device Driver and DDX for the DIGITAL UNIX X Server
- Kenton Lee: Technical X Window System and Motif WWW Sites
- RFC 1198 - FYI on the X Window System
